
Driven by an aging population, robotic surgery innovations, sensors and other technologies to detect costly periprosthetic joint infection, and a move to ambulatory surgery centers, the global orthopedic surgery market is on track to reach a value of nearly $70 billion by 2030.
The orthopedic surgery market, one of the largest medical device markets in the world, is evolving and expanding, with a global forecast value of nearly $70 billion by 2030, according to LSI’s Market Analysis and Projections (MAP) database. Device and surgical innovations are addressing unmet needs in this space, leading to a transformation in healthcare delivery, improvement in patient outcomes, and an enhancement in the overall quality of life for a growing patient population whose lives are limited by bad knees, hips, shoulders, and other joints.
Demographic factors contributing to demand for device innovation include a growing population over age 65 with degenerative joint diseases and injuries that are requiring prosthetic implants in order to maintain a high quality of life, and the obesity epidemic. Joint replacement is typically considered once other treatment options such as medication, physical therapy, and injections have been exhausted and a person is still experiencing significant pain and limited function in a joint due to conditions like arthritis— meaning it is considered a last resort when other alternatives are no longer effective. Better and more personalized implant technology and computer-assisted surgery systems including robotics and 3D printing, plus the cost-effective transition of many orthopedic surgeries to the ambulatory surgery center (ASC) setting, are also fueling demand and growth.
In 2024, 30.5 million orthopedic surgical procedures will be performed, a 4.5% increase from 2023, according to LSI’s Global Surgical Procedure Volumes database. Orthopedic surgeries rank as the second most-performed procedure globally, behind general surgeries at 75 million, and cardiovascular procedures coming in at number three with 24 million globally projected for 2024, according to LSI’s Market Intelligence Platform.
In 2024, 30.5 million orthopedic surgical procedures will be performed, a 4.5% increase from 2023, according to LSI’s Global Surgical Procedure Volumes database. Orthopedic surgeries rank as the second most-performed procedure globally, behind general surgeries at 75 million, and cardiovascular procedures coming in at number three with 24 million globally projected for 2024, according to LSI’s Market Intelligence Platform.
The top orthopedic surgery performed globally, by far, is extremity fracture repair, with a projected total of 15 million for 2024, that is more than double that of sports medicine arthroscopies at 6.4 million. Following that is knee arthroplasties (4 million; total, partial, or revision), hip arthroplasties (3.6 million; total, partial, or revision), and other joint arthroplasties (740,000).
During the forecast period 2023 to 2028, the fastest growing orthopedic procedures worldwide are forecast to be major joint arthroplasties, with shoulders growing at the greatest rate, a 9.4% compound annual growth rate (CAGR), according to LSI research. This growth rate is partially because they are the smallest volume procedure today (421,200 estimated procedures worldwide in 2023) in comparison to knees and hips, and also due to the rapid adoption of reverse shoulder arthroplasty for proximal humerus fractures (the second-most common fragility fracture in older adults), that has expanded the number of patients eligible to receive this procedure. Knee replacement procedures are also increasing rapidly, at a 6.7% CAGR, and hip replacements at a 5.5% CAGR, according to LSI projections.
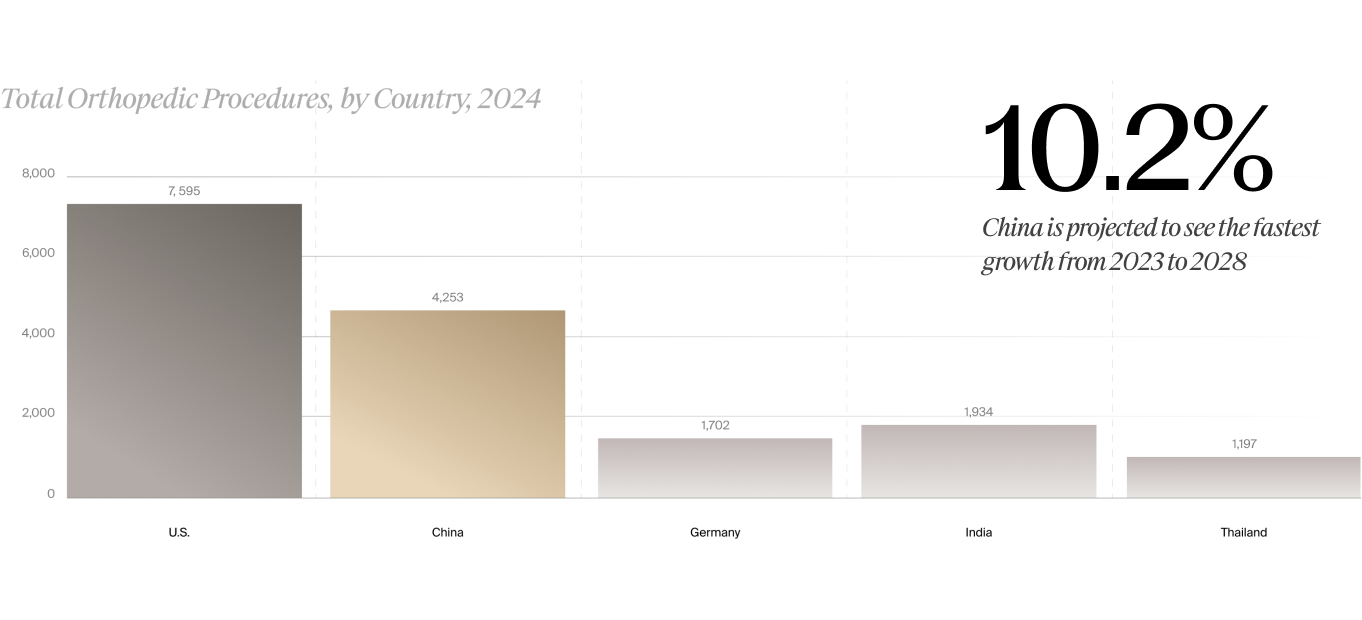
In terms of total orthopedic procedure volumes by country, the U.S. comprises the highest share, with 7.8 million total orthopedic procedures forecast for 2024, followed by China at 4.7 million, then India at 2 million, Germany with 1.7 million, and Thailand at 1.2 million, according to LSI’s global procedure volumes data. However, with a 10.2% annual growth rate, China is projected to surpass the U.S. in orthopedic procedure volumes after 2030, according to LSI (see figure).
Several factors are at play in the U.S., in addition to an aging population: the country has a well-developed healthcare system that makes procedures accessible, and also the growth of same-day ASCs. The number of surgical cases shifting from hospitals to ASCs continues to increase, particularly in the field of orthopedics, and these lower-cost settings represent a major growth driver for orthopedic surgeries over the next few years, as discussed later in this article.
Drilling down into the U.S. numbers, LSI expects orthopedic procedures to grow at a moderate rate of about 3.3% from 2023 to 2028. The fastest growing procedures include elbow, knee, and shoulder arthroplasties.
The four largest joint replacement players globally are Zimmer Biomet, Stryker, DePuy Synthes, and Smith & Nephew. The dominance of these players can be attributed to their diversified portfolios of joint implants for both upper and lower extremities, and their aggressive stance on new product launches and tuck-in acquisitions of complementary technologies to maintain their market position.
Innovation Driving Better Patient
Outcomes and Market Growth
Device and surgical innovations to improve the accuracy and longevity/durability of implant placements, and reduce costly revision surgeries and implant-related infections, are among the growth drivers in the global orthopedic device market. In the following sections, we examine some key enabling technologies and examples of companies that are working to shape the future of orthopedic surgery.
Robotics
Robotic arm-assisted arthroplasty was first introduced in orthopedics in 2006, and since that time the technique has been advancing to overcome technical challenges associated with manual procedures, increasing accuracy in alignment, and impacting clinical outcomes—in the knee in particular.
LSI and the device industry remain bullish on robotic-assisted orthopedic surgery, as the rapidly evolving innovation has already impacted general, gynecologic, urologic, and cardiothoracic surgery, to name a few. According to LSI’s estimates, the global orthopedic surgical robotics market in 2024 will reach $679 million.
Robotics has allowed for a number of advantages compared to traditional open surgery in orthopedics, particularly in the knee. This includes improved precision in surgery, as robotic arms provide real- time feedback and fine adjustments to ensure implants are positioned correctly and aligned with the patient’s anatomy. Robotics also enables personalized care, as the technology can tailor procedures to individual anatomical characteristics. Robotics can also minimize tissue damage and blood loss, especially with miniaturized technology, and facilitate minimally invasive procedures that can lead to fewer complications and revision surgeries (especially in combination with the use of customized implants), shorter hospital stays, and faster patient recovery. Robotics can also extend to postoperative rehabilitation, using exoskeletons and motion- capture systems to optimize mobility and strength recovery.
Advancements in near-field camera technology, device miniaturization, adaptive software algorithms, and AI and deep learning techniques for the optimization of surgical planning—including intraoperative plan adjustments—are poised to enhance all robotic surgery capabilities, including orthopedic, in clinically relevant ways. The overarching goal, according to LSI alum THINK Surgical, a Fremont, CA-based developer of a miniature, wireless, open (meaning that it is implant- and vendor-agnostic) robotic system for total knee replacement, is to drive efficiency, reduce the physical and cognitive burden on surgeons and operating room staff and, most importantly, ensure improved and consistent patient outcomes. In November, THINK Surgical announced that its TMINI Miniature Robotic System had received FDA 510(k) clearance for use with the Freedom Total Knee, Freedom Titan Knee, and Freedom Primary PCK Systems; the MOBIO Total Knee System; and the LinkSymphoKnee.
THINK Surgical’s implant-agnostic approach is a patient-centered trend and a real differentiator in this market niche, as individualized surgical plans for implant positioning and a more personalized approach to implant selection based on patient need aligns with the goal of robotic systems to improve patient outcomes.
THINK Surgical’s implant-agnostic approach is a patient-centered trend and a real differentiator in this market niche, as individualized surgical plans for implant positioning and a more personalized approach to implant selection based on patient need aligns with the goal of robotic systems to improve patient outcomes.
Another LSI alum innovator in this space, the French company eCential Robotics, has developed and received FDA 510(k) clearance for an open, unified, and scalable robotic surgery solution adapted to bone surgery procedures. Its platform is designed as a single system integrating 2D/3D imaging, navigation and robotics.
The leading suppliers of orthopedic robotic systems include some of the largest orthopedics companies in the world: Stryker, Zimmer Biomet and Smith & Nephew. Stryker’s Mako system (developed by Mako Surgical Corp., which was acquired by Stryker in 2013 for $1.65 billion) is a robotic arm-assisted platform designed for knee and hip replacements. It combines 3D planning with robotic precision to help surgeons create personalized surgical plans and execute them accurately and efficiently. Stryker has continued to develop its Mako system, enhancing its capabilities for total knee, partial knee, and hip replacements. The company is also investing in research and development to bring new robotic solutions to market.
Zimmer Biomet offers the ROSA Knee System, the ROSA Partial Knee System, and the ROSA Hip System, a robotic-assisted platform that helps surgeons personalize knee and hip replacement procedures, and improve procedure accuracy and efficiency. Zimmer Biomet acquired the ROSA robotics portfolio, which included spine and brain applications, as part of its 2016 acquisition of French robot-assisted surgery firm, Medtech. Zimmer Biomet then developed the knee application internally. In February of this year, the company received FDA 510(k) clearance for its ROSA Shoulder System for robotic- assisted shoulder replacement surgery, the world’s first robotic surgery system for this application.
Smith & Nephew, through its acquisition of Blue Belt Technologies in 2016, offers the Navio Surgical System, a handheld robotic system that assists surgeons in partial knee replacements. It uses a CTfree, image-guided approach for precise implant placement and alignment.
Robotic surgical systems for orthopedics and other specialties are continuously evolving to meet the needs of customers, including models that are transforming the same-day-surgery/ASC environment. Challenges still to be overcome include the high cost of purchasing and maintaining robotic systems, the often longer operating times, and the need for specialized training. In addition, a robotics approach is more often used for knee arthroplasties currently, versus hip and other joints. Larger, long-term, randomized controlled trials are needed to confirm their comparative effectiveness to other surgical techniques, and both short-term and long-term outcomes, and drive orthopedic procedure volumes in the coming years.
Infection Detection Technologies
Affecting over 40,000 people in the U.S. annually, periprosthetic joint infection (PJI) is a rare and potentially devastating complication of joint replacement surgery in which pathogenic bacteria colonize the joint prosthesis, forming difficult-to-remove structures called biofilms. Biofilm infections are challenging to resolve, requiring long, invasive and expensive treatments that are often unsuccessful, resulting in high rates of permanent disability and early death. Recent retrospective analyses demonstrate that the current gold standard for treatment of PJI, twostage exchange arthroplasty, takes an average of 16 weeks and has a success rate under 50% after 12 months, highlighting the unmet need for faster and more efficacious treatment options.
Worldwide, the cost of PJIs totals over $3.3 billion, to manage the 1-2% of joint replacement procedures that develop infec tions, according to LSI (see the sidebar for a compelling LSI “By the Numbers” examination of the estimated cost of infections in knee replacements alone). PJIs represent a significant health challenge, with standard of care treatment involving a costly two-stage revision surgery and prolonged rounds of antibiotics, which can profoundly disrupt a patient’s life. There is a need for better methods to treat these rare but significant complications.
One novel solution to detecting joint replacement health and spotting complications early is orthopedic implant sensors. These devices are embedded in implants and monitor a patient’s condition and the implant’s performance in real time. The sensors can detect changes in the patient’s physical environment, such as pressure, temperature, strain, and alignment. They can also detect changes in the implant’s biochemical environment.
Orthopedic implant sensors can be used for a variety of applications, including providing real-time information to help surgeons position the implant, post-operative monitoring for help optimize the healing process, detect implant loosening or failure, and reduce the need for hospital visits and secondary procedures, infection detection through the use of thermal sensors, and fracture healing monitoring. The data from the sensors is transmitted to an external device such as a computer, using Bluetooth or radiofrequency waves. The data can then be analyzed by clinicians to help them monitor the patient’s treatment and make timely interventions.
One innovator in this area, LSI alum Canary Medical, is giving a “voice” to implantable medical devices through the use of proprietary integrative sensor technology. Its Canturio platform “listens” to implanted devices and collects data to monitor device performance. The company has strategically partnered with ortho implant leader Zimmer Biomet and its Persona IQ Smart Knee.
A number of innovative companies are targeting the management of implant-related infections in different ways. These include Reselute, Osteal Therapeutics, and Solenic Medical.
Start-up Reselute, which is developing new approaches to deliver antibiotics locally to sites of orthopedic infection, closed a seed financing round in May 2023 led by Duke Capital Partners, the early-stage venture investment arm of Duke University.
Osteal Therapeutics, whose CEO David Thompson presented at LSI Europe ‘23, is a clinical-stage biopharmaceutical company developing a new category of combination drug/device therapies for orthopedic infections. It is leveraging the ability of concentrated, locally delivered antimicrobials to treat the bacterial biofilms typically responsible for musculoskeletal infections while minimizing off-target tissue exposure and associated adverse effects.
Osteal Therapeutics, whose CEO David Thompson presented at LSI Europe ‘23, is a clinical-stage biopharmaceutical company developing a new category of combination drug/device therapies for orthopedic infections. It is leveraging the ability of concentrated, locally delivered antimicrobials to treat the bacterial biofilms typically responsible for musculoskeletal infections while minimizing off-target tissue exposure and associated adverse effects.
Focusing on implant preservation, Solenic, whose CEO James Lancaster also presented at LSI Europe ‘23, is developing a non-invasive medical device that utilizes alternating magnetic fields to eradicate biofilms that form on implants. Solenic’s work on a non-invasive solution to tackle PJI has already captured the attention of heavy hitters like Johnson & Johnson. In July 2023, Solenic closed a $5.1M Series A led by Johnson & Johnson Innovation–JJDC, Inc.
Technology Innovation Supports
Shift to Ambulatory Surgery Centers
Advanced imaging and implant technologies, and minimally invasive surgical techniques have made ambulatory (aka outpatient or same-day) orthopedic surgery safer, more comfortable, and more cost-effective overall, and a replacement for hospital-based care in the majority of cases. In fact, initially fueled by surgical site of care challenges learned during the pandemic, orthopedics is one of the main categories of high-demand procedures being shifted to ASCs.
Another crucial driver for the move to ASCs: the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) has recently approved reimbursement for total shoulder replacements, total ankle replacement, hip tendon incision, meniscal knee replacement, and hip and knee arthroscopy, to name only a few of the musculoskeletal conditions when performed in these non-hospital settings.
Over the next 10 years, orthopedic surgical procedures at ASCs are projected to grow by at least 25%, primarily due to cost. Common procedures performed in hospital outpatient departments cost significantly more than in an ASC. In fact, an ASC can perform the same procedures for up to 144% less, due to increases in healthcare provider workflow by focusing on one specialty, and by avoiding hospital room charges, nursing services, and other hospital-related costs, according to studies.
And, these trends mean significant savings for the healthcare system. Non-Medicare patients choosing ASCs for procedures (all procedures combined, not just orthopedic) create $42.2 billion in annual savings in healthcare spending, while Medicare patients being cared for in an ASC setting result in $4 billion in annual savings, according to the Ambulatory Surgery Center Association (ASCA).
Medical device companies are also fostering growth in this area by catering to their ASC customers, including financing plans for equipment, special payment plans for pricier devices such as surgical robots, and dedicated sales teams.
3D Printing
While facing challenges similar to robotics, chiefly higher cost and lack of clinical data, in addition to regulatory and quality control concerns, 3D printing represents an accessible approach to custom implants designed to the patient’s specific physiology. By combining medical images from X-rays, CT, MRI, or ultrasonic scanning, 3D printing can be used to create patient-specific implants with almost the same anatomical structures as the injured tissues.
Potential benefits to this emerging specialty include faster recovery time for patients due to the precise fit of the custom implant, improved range of motion, better osteointegration due to the implant being made of alternatives to solid metal such as metal lattice material that promotes osteointegration, increased bone strength, and lower implant cost. 3D printing technology has been used to create implants for a variety of orthopedic procedures, including knee replacements, spine implants, and ankle replacements.
One innovator in this space is LSI alum restor3d, that has developed 3D printed, personalized orthopedic implants for use across the entire human body. The company leverages a proprietary porous implant architecture to encourage bone growth through the implant and maximize graft packing.
Bridging the Gap before Total Joint Replacement
Another innovative approach to improving patient outcomes and quality of life, specifically in patients with mild to moderate osteoarthritis who want to preserve their knee joints, has been developed by Fremont, CA-based Moximed.
The company’s FDA-cleared technology, the MISHA Knee System, is the first implantable shock absorber for the treatment of medial compartment knee osteoarthritis, bridging the gap between chronic knee pain and total knee arthroplasty. The polymer implant is placed on the medial knee and moves with the natural joint, reducing about 30% of the peak force on the knee with every walking step, according to the company.
And, investors believe in Moximed’s approach. This past August, Moximed closed on a $61 million Series D preferred stock financing, with an option to close on up to an additional $30 million. The round was led by Elevage Medical Technologies, a Patient Square Capital platform, with participation from new investors Cormorant Asset Management and Warren Point Capital and existing investors New Enterprise Associates (NEA), Future Fund, Advent Life Sciences, Gilde Healthcare, Vertex Ventures HC, GBS Venture Partners, and Morgenthaler Ventures.
Driven by the aging population, there is a huge unmet need to introduce solutions that, like Moximed’s technology, orthobiologics, and other innovative strategies, bridge the gap between chronic knee pain and joint replacement.









